“Our age not only does not have a very sharp eye for the almost imperceptible intrusions of grace, it no longer has much feeling for the nature of the violence which precede and follow them.” — Flannery O’Connor (as quoted in my previous post)
Flannery O’Connor made this remark back in 1963. It was not only a sharp social commentary and prophetic, but to me, it also stands as one of the signs of a good film. Amidst the violence and ugliness a film may depict, the presence of grace, however small, or a mere spot of purity, could bring out a powerful contrast. Usually that is what’s needed to emit a redemptive spark, offering a glimpse of light pointing to the transcendent.
With this frame of grace among violence, I go back to the films I’ve watched and try to find some good examples. My task proves to be more difficult than I first thought. But after some deep searching through my mental archive, several films came to mind. I’ll just mention two for this post.
**
Pickpocket (1959)
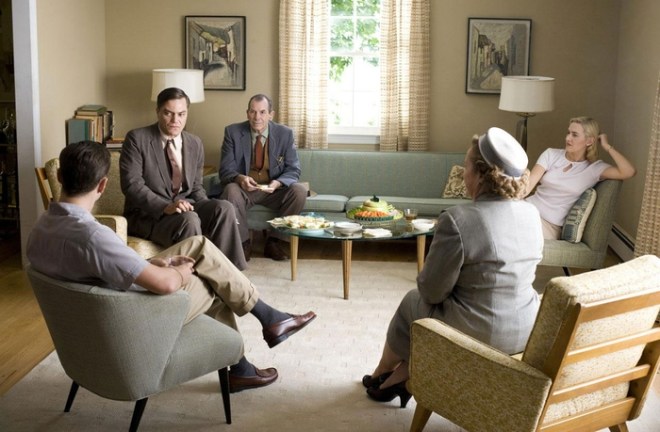
Robert Bresson’s modern version of Dostoevsky’s Crime and Punishment. Caught in his own desensitized internal world, our protagonist Michel commits acts of theft as a desperate measure to fill the void in his existence. He goes through his days in a haunting vacuum devoid of meaning and emotions. He is unfeeling even towards his own dying mother, reminds me of Meursault in Camus’s The Stranger. Although not an axe murderer, like Raskolnikov in Crime and Punishment, Michel theorizes that those with superior talents and intelligence, the supermen in society, should be free to disobey laws in certain cases. He is numbed by his own hubris, and stifled by his cold and absurd worldview. Outright violence is not visible here, but we see the battle of wits he engages with the police inspector behind his trails, and we see him struggle in an amoral and meaningless existence.
Grace comes as Jeanne, a neighbor and carer of Michel’s ailing mother. Jeanne lives on her own looking after her younger brother. Her father is a drunk and her mother has deserted them. But she continues to live and care. She accepts her circumstances calmly, and extends kindness to those unrelated to her, caring for Michel’s mother, a neighbor on another floor. She stands as a stark contrast to Michel’s aloofness. At the end of the film, Jeanne came to visit Michel in prison after he was arrested, the two separated by the cold iron bars. For the first time, Michel feels love and wants to reciprocate it. And thus the cathartic ending as he totally melts in the presence of pure love and grace, wrapping up the film with this last line:
“Oh, Jeanne, to reach you at last, what a strange path I had to take.”
.
Drive (2011)
A current release that comes with high acclaims. The film was nominated for the Palme d’Or and Nicolas Winding Refn won Best Director at the Cannes Film Festival this year. With slick and dashing camera work, the violence in “Drive” is visceral and graphic, a big contrast to the black and white, internal “Pickpocket”. However, I see some parallels between these two films made 50 years apart.
Ryan Gosling is “the Driver”. He does not even have a name. He is an expert stunt driver for movies and works at an autobody shop by day, drives a get-away car in the underworld of crimes by night. Like Michel in “Pickpocket”, he drifts in existence, numb and desensitized to the world around him. That is, until he meets Irene (Carey Mulligan), his neighbor.
Mulligan’s almost angelic presence in the film is most effective as a stark contrast to those around her. She lives alone looking after a child and works as a waitress in a diner. She appeals to the Driver by being herself, innocent, taking life as it is, responsible, caring for a child alone while her husband is locked up in prison. Irene is a spot of purity in a rough environment. Her mere presence has transformed the Driver. From being aloof the Driver has become engaged emotionally, friendly and protective of both mother and son.
The plot thickens as Irene’s husband is released from prison and rejoins his family. The Driver is caught in an awkward situation. But he soon realizes that the husband’s resolve for a new start is genuine. The power of transformation is so thorough that the Driver is willing to go out on a limb to help the husband with one last heist in order to break the hold a gang has on the man and his wife and kid. While things go awry terribly and the ending is not as clean-cut as “Pickpocket”, we learn that the Driver remains a changed man from the ephemeral friendship he once had with Irene and her child.
I’ve heard a critic say Mulligan is a miscast, that she’s not “damaged enough”, and would prefer a ‘stronger’ character. I disagree. I feel that Mulligan has portrayed Irene’s innocent persona aptly, and yes, those ethereal dimples can just melt any heart. Hers is the perfect role for exactly the right reason. In the dark underworld of gangs, violence and crimes, she stands out as a tiny source of purity, a spark of grace. It all shows that what may look weak and vulnerable can have transformative power over the strong. A thought that may well be unpopular today.
***
Other related posts from Ripple Effects:
A Good Man Is Hard To Find and Other Stories by Flannery O’Connor
Bernini’s Corpus and Modern Movies
Notes on the Synthesis of Film, Art… Life?